큐(Queue) 및 덱(DeQ) 구현
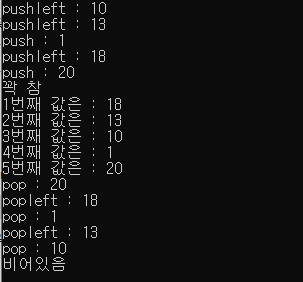
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 | #include <iostream> using namespace std; class deque { public: int size; int count = 0; int* arr; void setsize(int num) { size = num; }; void pushleft(int num) { if (isFull()) { cout << "꽉 참" << "\n"; return; } cout << "pushleft : " << num<< "\n"; for (int i = count; i >= 0; i--) { arr[i+1] = arr[i]; } arr[0] = num; count++; } void push(int num) { if (isFull()) { cout << "꽉 참"<<"\n"; return ; } cout << "push : " << num <<"\n"; arr[count ++] = num; }; void print() { if (isEmpty()) { cout << "비어있음\n"; return; } for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { cout << i + 1 << "번째 값은 : " << arr[i] << "\n"; } } int pop() { if (isEmpty()) { cout << "비어있음\n"; return -1; } cout << "pop : " << arr[--count] << "\n"; return arr[count]; } int popleft() { if (isEmpty()) { cout << "비어있음\n"; return -1; } cout << "popleft : " << arr[0] << "\n"; int pop = arr[0]; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { arr[i] = arr[i+1]; } count--; return pop; } bool isEmpty() { if (count == 0) { return true; } else { return false; } } bool isFull() { if (count == size) { return true; } else { return false; } } }; deque create(int num) { int *arrt = new int[num]; //동적 배열 생성 deque stk; stk.setsize(num); stk.arr = arrt; return stk; } int main() { deque stk = create(5); //5 크기의 스택 생성 stk.pushleft(10); stk.pushleft(13); stk.push(1); stk.pushleft(18); stk.push(20); stk.push(2); //예외 발생 stk.print(); stk.pop(); stk.popleft(); stk.pop(); stk.popleft(); stk.pop(); stk.pop(); //예외 발생 } | cs |
실행 결과